Proprietary Ratio: Understanding Equity Ratio and Solvency Implications
Shareholders’ funds include equity, preference share capital, profits or losses, reserves, and surplus. It is a solvency ratio as you are essentially measuring the strength of a company’s capital structure. Since it is funding most of its assets using shareholder equity, the company creditors will not be exposed to liquidity risk or default risk.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Debt Covenant Compliance Calculations
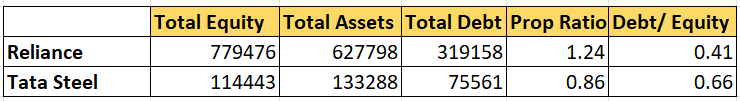
Which, if you see that Reliance has lower debt compared to tata steel, but has a high proprietary ratio. On the other hand, if the ratio is low, it means that the company may be using more debt to support its business than equity. Out of current assets, inventories and prepaid expenses are not included because these cannot be converted into cash easily. To answer the question in the title, this article defines, explains, and provides examples of all the importance balance sheet ratios. If the company has too much debt, creditors may fear liquidity issues in case the company’s cash flows fluctuate or something happens to the company.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
- A large portion of debts in the total capital may reduce creditors interest, increase interest expenses and also the risk of bankruptcy.
- Total assets refers to a company’s total assets on its balance sheet regardless of how it was funded (through debt or equity).
- The ratio is relevant for investors and creditors interested in understanding how much a company relies on equity rather than debt financing.
- High leverage may expose a company to financial risks, which creditors need to monitor closely.
- Understanding the proprietary ratio aids in evaluating the capital structure and financial stability of a business.
The free file your income tax return of 64% means, 64% of the total assets of the company are financed by proprietors’ funds. Proprietors’ funds include share capital, reserves and surpluses as per the balance sheet. The ideal ratio of proprietary ratio depends on the nature of the business as well as the investor’s risk appetite. The result will be more accurate of the company’s valid condition if you exclude goodwill and intangible assets from the denominator. The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is a measure of how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings.
How Does GooglePay Earn Money? (GooglePay Business Model Revealed)
It helps to determine the financial strength of a company & is useful for creditors to assess the ratio of shareholders’ funds employed out of total assets of the company. The proprietary ratio indicates the proportion of total assets financed by equity rather than debt. When financial leverage increases, the proprietary ratio decreases, signaling that the company is relying more on borrowed funds. High leverage may expose a company to financial risks, which creditors need to monitor closely.
Understanding the Proprietary Ratio: Meaning, Formula, and Significance
It helps to determine the financial strength of a company & is useful for creditors to assess the ratio of shareholders’ funds employed out of the total assets of the company. A low proprietary ratio shows that a larger portion of the company’s total assets is funded by debt thereby increasing the company’s default risk (which is not favorable for investors and creditors). Creditors need assurance that the businesses they finance are capable of repaying loans and interest over time.
Debt-Service Coverage Ratio (or Interest Coverage Ratio)
The proprietary ratio measures the contribution of shareholders or proprietors toward the company’s total assets, providing a clear indication of financial stability. Companies with a high proprietary ratio are seen as less risky, as they rely more on equity financing than debt, reducing the likelihood of default. The Proprietary Ratio, also known as the equity ratio, is a financial metric that indicates the proportion of a company’s total assets that are financed or owned by the owners or shareholders.

If the company’s proprietary ratio is low, investors and company stakeholders should further assess the company’s liquidity to see if the company presents solvency risks. Also, you should consider the company’s cash flow statements to see if there are one-time events or other events that may have impacted the proprietary ratio. When you have a high proprietary ratio, it means that the company is in a good financial position. It’s also important to note that some businesses, such as capital-intensive industries, may require substantial debt financing while maintaining high profitability. Therefore, relying solely on this ratio to evaluate such companies may not be appropriate. Ultimately, it is up to investors and proprietors to determine the appropriate balance of equity and debt financing based on their risk tolerance and investment goals.
The proprietary ratio is essential for investors and creditors to assess a company’s long-term financial stability. A high ratio indicates that the company relies less on debt, leading to a stronger balance sheet and reduced financial risk. It’s particularly useful for comparing companies in the same industry or tracking a company’s financial structure over time. The proprietary ratio holds great significance for creditors as it serves as a vital tool to assess the financial stability of a company. By measuring the extent to which a company’s total assets are financed by shareholders’ equity rather than debt, creditors gain valuable insight into the company’s risk profile.
For example, an excessively high ratio can mean that management has not taken advantage of any debt financing, so the company is using nothing but expensive equity to fund its operations. Instead, there is a balance between too high and too low a ratio, which is not easy to discern. A low proprietary ratio signifies that more use debt funds for purchasing total assets. By looking at Company ABC’s financial statements, we can see that it has a shareholders’ equity of $5,000,000.
The term liquidity refers to the ability of a company to pay its short-term liabilities as and when they are due for payment. In this article, the readers will be able to know about the proprietary ratio in detail, along with certain other topics. Or 75% meaning hereby that 25% of the funds have been supplied by the outside creditors. Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.



Leave a Reply